X 2 9x 10 0
disgrace
Sep 18, 2025 · 6 min read
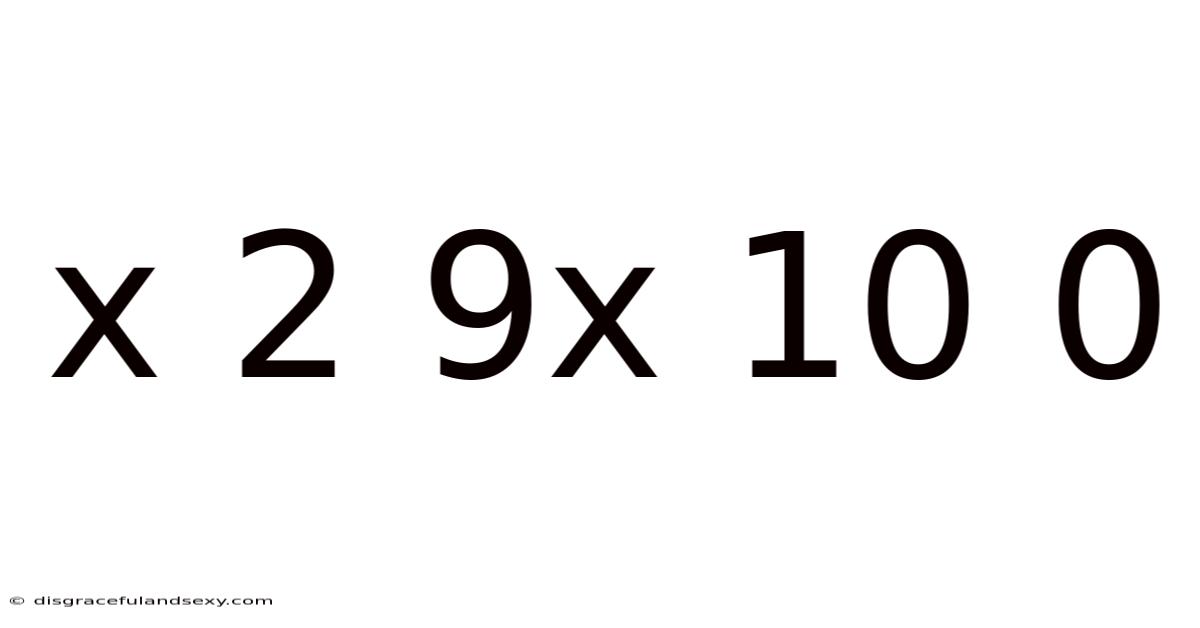
Table of Contents
Decoding the Mystery: x² + 9x + 10 = 0
This article delves into the intricacies of solving the quadratic equation x² + 9x + 10 = 0. We'll explore various methods, from factoring to the quadratic formula, providing a comprehensive understanding suitable for students of all levels. We'll also discuss the significance of quadratic equations in mathematics and their applications in real-world scenarios. Understanding this seemingly simple equation unlocks a gateway to more complex mathematical concepts.
Introduction: Understanding Quadratic Equations
A quadratic equation is a polynomial equation of the second degree, meaning the highest power of the variable (usually 'x') is 2. The general form of a quadratic equation is ax² + bx + c = 0, where 'a', 'b', and 'c' are constants, and 'a' is not equal to zero (otherwise, it wouldn't be a quadratic equation). Our specific equation, x² + 9x + 10 = 0, fits this form perfectly, with a = 1, b = 9, and c = 10. Solving this equation means finding the values of 'x' that make the equation true.
These equations are fundamental in various fields, including physics (projectile motion, oscillations), engineering (designing structures, analyzing circuits), and economics (modeling growth and decay). Mastering the techniques to solve quadratic equations is crucial for success in these and other related disciplines.
Method 1: Factoring the Quadratic Equation
Factoring is a powerful and often the quickest method to solve quadratic equations, particularly when the equation is easily factorable. The goal is to rewrite the equation as a product of two simpler expressions. For x² + 9x + 10 = 0, we look for two numbers that add up to 9 (the coefficient of x) and multiply to 10 (the constant term).
These two numbers are 5 and 4. Therefore, we can factor the quadratic as:
(x + 5)(x + 4) = 0
This equation is true if either (x + 5) = 0 or (x + 4) = 0. Solving these simpler equations gives us our solutions:
- x + 5 = 0 => x = -5
- x + 4 = 0 => x = -4
Therefore, the solutions to the quadratic equation x² + 9x + 10 = 0 are x = -5 and x = -4. These are also known as the roots or zeros of the equation.
Method 2: Using the Quadratic Formula
The quadratic formula is a universal method that works for all quadratic equations, regardless of whether they are easily factorable. It provides a direct way to calculate the roots, even when factoring proves difficult or impossible. The formula is derived from completing the square method and is expressed as:
x = [-b ± √(b² - 4ac)] / 2a
Substituting the values from our equation (a = 1, b = 9, c = 10) into the quadratic formula, we get:
x = [-9 ± √(9² - 4 * 1 * 10)] / (2 * 1) x = [-9 ± √(81 - 40)] / 2 x = [-9 ± √41] / 2
This gives us two solutions:
- x = (-9 + √41) / 2 ≈ -1.702
- x = (-9 - √41) / 2 ≈ -7.298
While these solutions are not integers like those obtained through factoring, they are equally valid solutions to the equation. The slight difference arises from the limitations of rounding decimal numbers during calculation. Note that using a calculator that shows multiple decimal places will provide more accurate results.
Method 3: Completing the Square
Completing the square is another algebraic method for solving quadratic equations. This method involves manipulating the equation to create a perfect square trinomial, which can then be easily factored. Let's apply this method to our equation:
x² + 9x + 10 = 0
-
Move the constant term to the right side: x² + 9x = -10
-
Take half of the coefficient of x (9/2 = 4.5), square it (4.5² = 20.25), and add it to both sides: x² + 9x + 20.25 = -10 + 20.25 x² + 9x + 20.25 = 10.25
-
Factor the left side as a perfect square trinomial: (x + 4.5)² = 10.25
-
Take the square root of both sides: x + 4.5 = ±√10.25
-
Solve for x: x = -4.5 ± √10.25 x ≈ -1.702 or x ≈ -7.298
As you can see, this method also leads to the same solutions obtained using the quadratic formula. While it might seem more involved than factoring or using the quadratic formula directly in this specific case, completing the square is a valuable technique that underpins the derivation of the quadratic formula itself and is crucial for understanding certain conic sections and other advanced mathematical concepts.
Graphical Representation and the Discriminant
The solutions of a quadratic equation also represent the x-intercepts (where the graph crosses the x-axis) of the parabola that represents the quadratic function y = x² + 9x + 10. The parabola opens upwards because the coefficient of x² (a = 1) is positive. The graph visually confirms that the parabola intersects the x-axis at two points, corresponding to the two solutions we found.
The discriminant, denoted as Δ (delta) and calculated as b² - 4ac, provides information about the nature of the roots.
- Δ > 0: Two distinct real roots (as in our case).
- Δ = 0: One real root (a repeated root).
- Δ < 0: Two complex roots (involving imaginary numbers).
In our equation, Δ = 9² - 4 * 1 * 10 = 41 > 0, confirming the existence of two distinct real roots.
Real-World Applications of Quadratic Equations
Quadratic equations are far from abstract mathematical concepts; they have extensive real-world applications:
-
Physics: Calculating the trajectory of a projectile (like a ball thrown in the air), analyzing simple harmonic motion (like a pendulum's swing), and understanding the motion of objects under constant acceleration.
-
Engineering: Designing parabolic antennas, determining the optimal dimensions for structures, and modeling the behavior of electrical circuits.
-
Business and Economics: Modeling profit, revenue, and cost functions, predicting market trends, and analyzing growth and decay patterns.
-
Computer Graphics: Creating curved shapes and smooth transitions in computer-generated images and animations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What if the quadratic equation doesn't factor easily?
A1: If factoring is difficult, you can always rely on the quadratic formula or completing the square. These methods always work, regardless of the nature of the roots.
Q2: What are complex roots?
A2: Complex roots occur when the discriminant (b² - 4ac) is negative. These roots involve the imaginary unit i, where i² = -1. They represent solutions that aren't directly representable on the real number line.
Q3: Can a quadratic equation have only one root?
A3: Yes, if the discriminant is zero (b² - 4ac = 0), the quadratic equation has only one real root, often referred to as a repeated root. This occurs when the parabola touches the x-axis at only one point.
Q4: How can I check if my solutions are correct?
A4: Substitute each solution back into the original equation. If both sides of the equation are equal, then the solution is correct.
Conclusion: Mastering Quadratic Equations
Solving the quadratic equation x² + 9x + 10 = 0, seemingly a simple task, opens doors to a deeper understanding of algebra and its wide-ranging applications. We've explored three different solution methods: factoring, the quadratic formula, and completing the square, highlighting their respective strengths and applications. Remember that the ability to solve quadratic equations is a cornerstone skill for success in various scientific, engineering, and economic disciplines. By understanding the underlying principles and mastering the various solution techniques, you're well-equipped to tackle more complex mathematical challenges in the future. The journey of mathematical understanding is a continuous process of exploration and discovery, and this equation serves as a stepping stone to further mathematical adventures.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about X 2 9x 10 0 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.