X 2 X 3 Expand
disgrace
Sep 21, 2025 · 5 min read
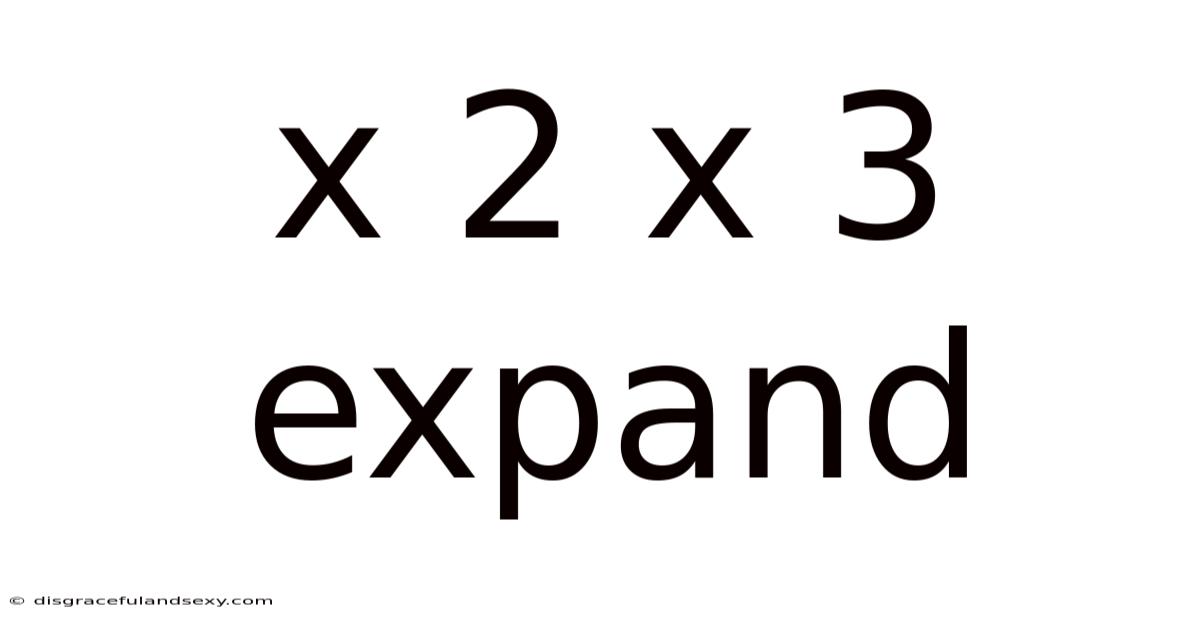
Table of Contents
Exploring the Expansion of x² x ³: A Deep Dive into Algebraic Multiplication
Understanding how to expand algebraic expressions like x² x ³ is fundamental to success in algebra and beyond. This seemingly simple expression holds the key to grasping more complex mathematical concepts. This article will provide a comprehensive guide to expanding x² x ³, exploring its underlying principles, demonstrating various approaches, and addressing common questions. We'll move beyond the simple answer to delve into the why and how, equipping you with a solid understanding of algebraic manipulation.
Introduction: The Fundamentals of Algebraic Multiplication
Before we tackle the expansion of x² x ³, let's review the basics of algebraic multiplication. The core principle lies in understanding that variables, represented by letters like 'x,' are placeholders for unknown numbers. When multiplying algebraic terms, we multiply the coefficients (the numbers in front of the variables) and add the exponents of the variables with the same base.
For instance:
- 2x * 3x = 6x² (2*3 = 6 and x¹ + x¹ = x²)
- 4x² * 5x³ = 20x⁵ (4*5 = 20 and x² + x³ = x⁵)
- -x * 2x² = -2x³ (-1*2 = -2 and x¹ + x² = x³)
These examples highlight the core rules. Remember that if a variable doesn't have a visible exponent, it's implicitly raised to the power of 1 (e.g., x = x¹).
Expanding x² x ³: The Step-by-Step Approach
Now, let's apply these principles to expand x² x ³. The expression represents the multiplication of two terms: x² and x³.
Step 1: Identify the Coefficients and Variables
Both terms have a coefficient of 1 (implicitly, as it's not written). The variable in both terms is 'x,' with exponents 2 and 3 respectively.
Step 2: Multiply the Coefficients
1 * 1 = 1
Step 3: Add the Exponents of the Variables
The base is 'x'. We add the exponents: 2 + 3 = 5
Step 4: Combine the Results
Combining the coefficient and the variable with its exponent, we get: 1x⁵, which simplifies to x⁵.
Therefore, the expanded form of x² x ³ is x⁵.
The Rule of Exponents and its Application
The process of adding exponents when multiplying terms with the same base is a direct application of the power rule of exponents. This rule states that a<sup>m</sup> * a<sup>n</sup> = a<sup>m+n</sup>, where 'a' is the base and 'm' and 'n' are the exponents. Our example, x² x ³, perfectly illustrates this rule. 'x' is our base, '2' is 'm,' and '3' is 'n.' Therefore, x² x ³ = x<sup>2+3</sup> = x⁵.
Understanding this rule is crucial not only for expanding simple expressions but also for tackling more complex problems involving polynomials, equations, and other advanced mathematical concepts. It is a fundamental building block upon which many other algebraic principles are built.
Beyond the Basics: Expanding More Complex Expressions
While x² x ³ is a straightforward example, let's extend our understanding to more complex scenarios. Consider the following examples:
-
2x² * 3x³y: Here, we have multiple variables. We multiply the coefficients (2 * 3 = 6), add the exponents of the 'x' variable (2 + 3 = 5), and keep the 'y' variable as it is, resulting in 6x⁵y.
-
(x²y)³: This involves raising a term with multiple variables to a power. We apply the power of a product rule: (ab)ⁿ = aⁿbⁿ. So, (x²y)³ = (x²)³ * (y)³ = x⁶y³.
-
(2x + 3)(x² - 4): This involves expanding a binomial multiplied by a binomial, requiring the FOIL method (First, Outer, Inner, Last). Let’s expand it step-by-step:
- First: (2x)(x²) = 2x³
- Outer: (2x)(-4) = -8x
- Inner: (3)(x²) = 3x²
- Last: (3)(-4) = -12
Combining these terms, we obtain 2x³ + 3x² - 8x - 12.
These examples demonstrate that the principles applied to x² x ³ extend to more intricate expressions. The key is to systematically apply the rules of coefficients and exponents, breaking down complex problems into manageable steps.
Connecting to Real-World Applications
While abstract, the principles of algebraic multiplication find practical applications across various fields. Examples include:
-
Physics: Calculating areas, volumes, and other physical quantities often involve algebraic expressions and their manipulation.
-
Engineering: Designing structures, analyzing circuits, and modeling systems often require working with complex algebraic equations.
-
Computer Science: Algorithm design, data structures, and software development frequently use algebraic concepts.
-
Finance: Calculating compound interest and analyzing investment growth often involves exponential expressions which build upon the foundation of exponent rules.
Understanding algebraic manipulation, therefore, is not merely an academic exercise but a critical skill set applicable to many real-world problems.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What happens if the bases are different?
A1: The rule of adding exponents only applies when the bases are the same. If you have, for example, x² * y³, you cannot combine the exponents. The expression remains as x²y³.
Q2: Can I expand x² x ³ using a different method?
A2: While adding exponents is the most efficient method, you could visualize it as repeated multiplication. x² x ³ can be written as (xx)(xx*x), which simplifies to x⁵. However, this method becomes less practical with higher exponents.
Q3: What if there are negative exponents?
A3: The rule still applies. For instance, x² * x⁻³ = x<sup>2+(-3)</sup> = x⁻¹. Remember that x⁻¹ = 1/x.
Q4: What are the common mistakes to avoid?
A4: Common mistakes include: * Multiplying exponents instead of adding them when multiplying terms with the same base. * Forgetting that a variable without a visible exponent has an implied exponent of 1. * Incorrectly applying the rules when dealing with multiple variables or negative exponents.
Conclusion: Mastering Algebraic Expansion
Mastering the expansion of algebraic expressions, starting with simple examples like x² x ³, is crucial for building a strong foundation in mathematics. It's not simply about memorizing a rule; it's about understanding the underlying principles of coefficients, exponents, and the power rule. By practicing and applying these concepts, you will confidently tackle more complex problems and open doors to a deeper understanding of advanced mathematical topics and their real-world applications. Remember to break down complex problems into manageable steps, and don't hesitate to review the fundamental rules when facing challenges. With consistent practice and attention to detail, you will master this crucial algebraic skill.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about X 2 X 3 Expand . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.