X 2 X 6 Factored
disgrace
Sep 11, 2025 · 6 min read
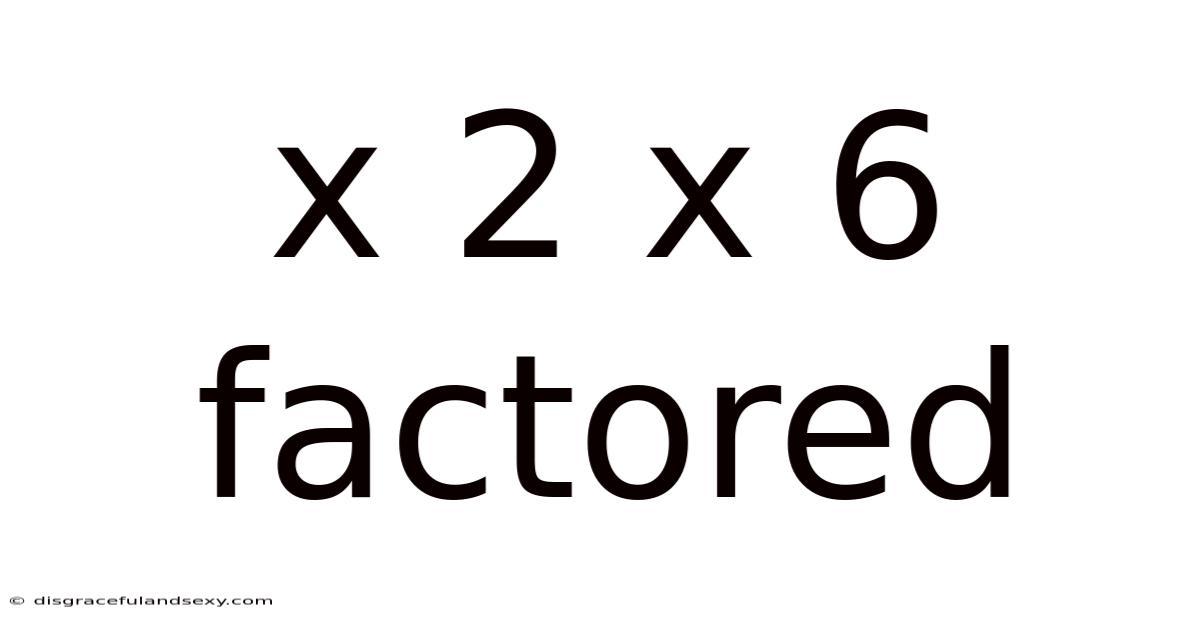
Table of Contents
Understanding and Factoring x² + 6x
This article delves into the process of factoring the quadratic expression x² + 6x. We'll explore different methods, explain the underlying mathematical principles, and provide clear examples to solidify your understanding. Factoring quadratic expressions is a fundamental skill in algebra, crucial for solving equations, simplifying expressions, and tackling more advanced mathematical concepts. By the end of this article, you'll confidently factor similar expressions and grasp the broader implications of this algebraic technique.
Introduction: What Does Factoring Mean?
Factoring, in the context of algebra, involves breaking down a mathematical expression into simpler components that, when multiplied together, produce the original expression. Think of it like reverse multiplication. Just as 12 can be factored into 2 x 6 or 3 x 4, algebraic expressions can also be factored. Factoring x² + 6x means finding two expressions that, when multiplied, result in x² + 6x. This skill is essential for solving quadratic equations and simplifying complex algebraic expressions.
Method 1: Greatest Common Factor (GCF)
The simplest approach to factoring x² + 6x is to identify the greatest common factor (GCF) shared by both terms. In this case, both terms, x² and 6x, contain a common factor of 'x'. We can factor out this 'x' to obtain:
x² + 6x = x(x + 6)
This is the factored form of the expression. To verify, we can expand this factored form using the distributive property:
x(x + 6) = xx + x6 = x² + 6x
This confirms that our factoring is correct. The GCF method is straightforward and efficient when applicable. However, it's important to note that this method only works if there is a common factor present in all terms of the expression.
Method 2: Completing the Square (for more complex scenarios)
While the GCF method was sufficient for x² + 6x, let's examine the more general method of completing the square. This method is particularly useful when dealing with quadratic expressions that don't readily reveal a common factor or when tackling more complex quadratic equations. Completing the square involves manipulating the expression to create a perfect square trinomial, which can then be easily factored.
To complete the square for x² + 6x, follow these steps:
-
Identify the coefficient of the x term: In x² + 6x, the coefficient of x is 6.
-
Halve the coefficient: Half of 6 is 3.
-
Square the result: 3 squared is 9.
-
Add and subtract the squared value: We add and subtract 9 to the expression to maintain its original value: x² + 6x + 9 - 9
-
Factor the perfect square trinomial: The first three terms, x² + 6x + 9, form a perfect square trinomial that factors to (x + 3)².
-
Rewrite the expression: The expression now becomes (x + 3)² - 9.
While this doesn't directly give us the same factored form as the GCF method, it demonstrates a powerful technique applicable to more complex scenarios where a simple GCF isn't apparent. This method is particularly useful when solving quadratic equations using the method of completing the square to find the roots.
Understanding Quadratic Equations and their Relationship to Factoring
The expression x² + 6x often appears within the context of quadratic equations. A quadratic equation is an equation of the form ax² + bx + c = 0, where a, b, and c are constants, and a ≠ 0. In our case, we have a simplified version where c = 0.
To solve a quadratic equation, factoring plays a crucial role. If we can factor the quadratic expression, we can then use the zero-product property: If the product of two factors is zero, then at least one of the factors must be zero.
For example, if we have the equation x² + 6x = 0, we can factor it as x(x + 6) = 0. Using the zero-product property, we get two possible solutions:
- x = 0
- x + 6 = 0 => x = -6
These are the roots or solutions to the quadratic equation. Therefore, factoring is not just a mathematical manipulation; it's a crucial tool for finding solutions to equations.
Expanding on Factoring: More Complex Quadratic Expressions
While x² + 6x is a relatively simple example, the principles of factoring extend to more complex quadratic expressions. Let's consider some examples and explore how the techniques we've learned can be adapted:
-
Example 1: 2x² + 12x: Here, we can factor out the GCF of 2x, resulting in 2x(x + 6).
-
Example 2: x² + 7x + 12: This requires a different approach. We need to find two numbers that add up to 7 (the coefficient of x) and multiply to 12 (the constant term). These numbers are 3 and 4. Therefore, the factored form is (x + 3)(x + 4).
-
Example 3: x² - 4x: Here, the GCF is x, giving us x(x - 4).
-
Example 4: x² - 9: This is a difference of squares, factoring to (x + 3)(x - 3). This is a special case that's important to recognize.
These examples highlight the versatility of factoring and demonstrate that different methods might be required depending on the structure of the quadratic expression. The GCF method remains a valuable first step, always checking for common factors before attempting other techniques.
The Importance of Practice and Further Exploration
Mastering the art of factoring requires consistent practice. Start with simple examples like x² + 6x and gradually work your way up to more challenging quadratic expressions. Don't hesitate to consult textbooks, online resources, and educational videos to supplement your learning. The more you practice, the quicker and more confidently you will be able to factor these expressions.
Beyond factoring simple quadratics, explore the following:
-
Factoring cubic and higher-order polynomials: The principles of factoring extend to polynomials of higher degrees, although the techniques become increasingly complex.
-
The quadratic formula: This formula provides a direct method for finding the roots of any quadratic equation, even those that are difficult or impossible to factor.
-
Complex numbers: Some quadratic equations have roots that are complex numbers (involving the imaginary unit 'i'). Understanding how to deal with complex roots is essential for a comprehensive understanding of quadratic equations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: What if I can't find a common factor? A: If you can't find a common factor, you might need to use more advanced techniques like completing the square or the quadratic formula. Sometimes, the expression might be prime (cannot be factored further using real numbers).
-
Q: Is there only one way to factor a quadratic expression? A: Generally, there is only one fully factored form for a given quadratic expression (ignoring the order of the factors). However, there might be different intermediate steps or approaches leading to the same final factored form.
-
Q: Why is factoring important? A: Factoring is crucial for solving quadratic equations, simplifying algebraic expressions, and solving problems in various fields like physics, engineering, and economics where quadratic relationships frequently arise.
-
Q: What if the quadratic expression is already in factored form? A: If it's already factored (e.g., (x+2)(x+4)), then you don't need to do anything further unless you need to expand it back into its standard form (x² + 6x + 8 in this example).
Conclusion: Mastering Factoring for Algebraic Success
Factoring the expression x² + 6x, whether through the simple GCF method or the more general completing the square method, provides a foundation for understanding and solving more complex algebraic problems. It's a fundamental skill that unlocks solutions to quadratic equations and simplifies many algebraic manipulations. Consistent practice and exploration of related concepts will solidify your understanding and boost your confidence in tackling a wide array of algebraic challenges. Remember that mastering algebra is a journey, and each step, like factoring x² + 6x, contributes to a broader understanding of mathematical principles and their applications.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about X 2 X 6 Factored . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.