X 3 4x 2 2
disgrace
Sep 13, 2025 · 6 min read
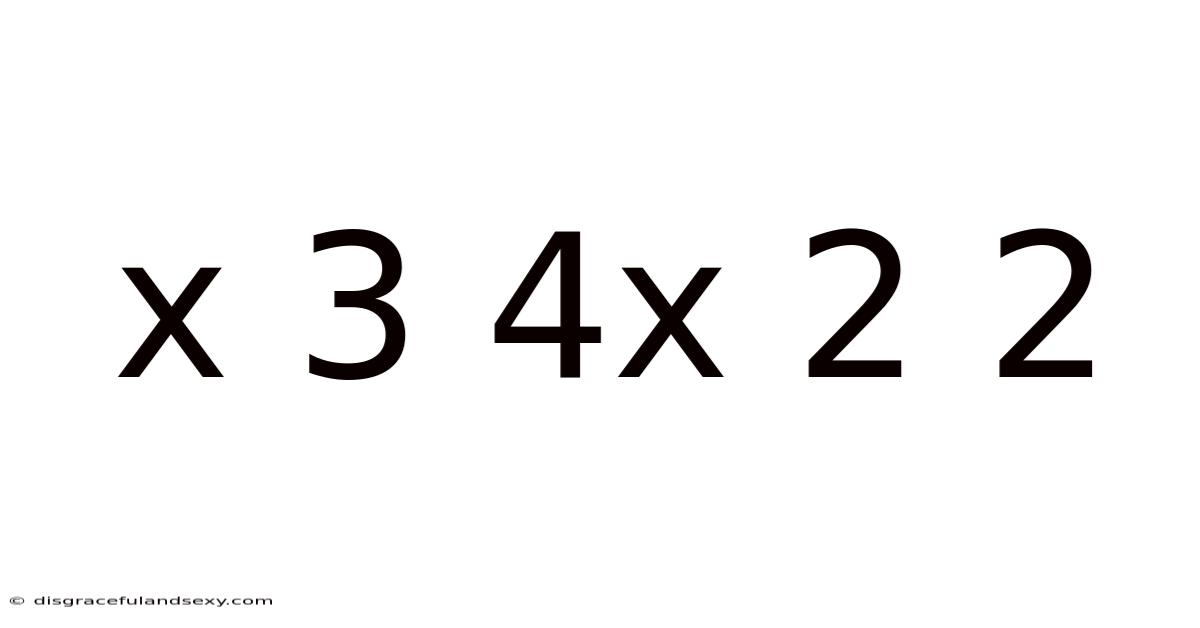
Table of Contents
Decoding the Mathematical Expression: x³ + 4x² + 2x + 2
This article delves into the mathematical expression x³ + 4x² + 2x + 2, exploring its properties, potential solutions, and applications. We'll examine how to approach this cubic polynomial, understand its behavior, and explore methods for finding its roots (or zeros). This comprehensive guide is suitable for students and anyone interested in deepening their understanding of algebra and polynomial functions.
Introduction: Understanding Cubic Polynomials
A cubic polynomial is a polynomial of degree three, meaning the highest power of the variable (in this case, x) is 3. Our expression, x³ + 4x² + 2x + 2, falls into this category. Understanding cubic polynomials is crucial in various fields, including physics, engineering, and economics, where they model various phenomena and relationships. This particular polynomial presents a challenge because there isn't an immediately obvious factorization. We'll explore various methods to analyze and potentially solve it.
Exploring the Polynomial's Behavior
Before attempting to find the roots, let's understand the general behavior of this cubic polynomial. We can analyze its characteristics based on its coefficients:
-
Leading Coefficient: The leading coefficient is 1 (the coefficient of x³). A positive leading coefficient indicates that the polynomial will increase towards positive infinity as x approaches positive infinity and decrease towards negative infinity as x approaches negative infinity.
-
Constant Term: The constant term is 2. This is the y-intercept of the function; the graph will intersect the y-axis at the point (0, 2).
-
Turning Points: A cubic polynomial can have at most two turning points (local maxima or minima). The exact locations of these turning points require calculus (finding the derivative and setting it to zero), but visually inspecting the graph (using a graphing calculator or software) can provide a good approximation.
Methods for Finding Roots (Solutions)
Finding the roots of a cubic polynomial can be more complex than finding the roots of a quadratic polynomial. There isn't a single, straightforward formula like the quadratic formula. However, several methods can be employed:
-
Rational Root Theorem: This theorem helps identify potential rational roots (roots that are rational numbers – fractions or integers). For our polynomial, x³ + 4x² + 2x + 2, the possible rational roots are the factors of the constant term (2) divided by the factors of the leading coefficient (1). Therefore, the potential rational roots are ±1 and ±2. We can test these values by substituting them into the polynomial:
- If x = 1: 1³ + 4(1)² + 2(1) + 2 = 9 ≠ 0
- If x = -1: (-1)³ + 4(-1)² + 2(-1) + 2 = 3 ≠ 0
- If x = 2: 2³ + 4(2)² + 2(2) + 2 = 26 ≠ 0
- If x = -2: (-2)³ + 4(-2)² + 2(-2) + 2 = 2 ≠ 0
None of the potential rational roots are actual roots. This indicates that the roots are likely irrational or complex numbers.
-
Numerical Methods: When analytical methods fail to provide exact solutions, numerical methods provide approximate solutions. These methods, often implemented using computer software or calculators, include:
- Newton-Raphson Method: An iterative method that refines an initial guess to find a root.
- Bisection Method: A method that repeatedly halves an interval containing a root.
- Secant Method: Similar to the Newton-Raphson method but doesn't require the derivative.
These methods require an initial guess, and their accuracy depends on the chosen method and the number of iterations.
-
Cubic Formula: Similar to the quadratic formula, there exists a cubic formula for solving cubic equations. However, it's considerably more complex and often impractical to apply manually. It's generally more efficient to use numerical methods or consider other approaches.
-
Graphing: Graphing the polynomial can visually identify approximate locations of the roots. By observing where the graph intersects the x-axis, we can obtain estimates of the roots. This method is valuable for gaining an understanding of the polynomial's behavior and providing initial guesses for numerical methods.
Further Analysis: Complex Roots and the Fundamental Theorem of Algebra
Since our attempts to find rational roots were unsuccessful, it's highly likely that the polynomial possesses at least one irrational or complex root. The Fundamental Theorem of Algebra states that a polynomial of degree n has exactly n roots (counting multiplicity), and these roots can be real or complex numbers. Since our polynomial is of degree 3, it must have three roots.
The nature of these roots (real, irrational, or complex) can be further investigated using more advanced techniques such as:
- Cardano's Method: A method for solving cubic equations that explicitly deals with complex roots.
- Discriminant: The discriminant of a cubic polynomial can indicate the nature of its roots (all real, two real and one complex, or all complex). Calculating the discriminant requires a more involved formula.
Applications of Cubic Polynomials
Cubic polynomials have widespread applications across numerous fields:
- Engineering: Designing curves for roads, bridges, and other structures.
- Physics: Modeling projectile motion, oscillations, and other physical phenomena.
- Economics: Analyzing cost functions, revenue functions, and profit maximization.
- Computer Graphics: Creating smooth curves and surfaces.
- Chemistry: Modeling chemical reactions and equilibrium.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: Is there a simple formula to solve x³ + 4x² + 2x + 2?
- A: No, there isn't a simple formula like the quadratic formula. Numerical methods or the more complex cubic formula are necessary.
-
Q: What does it mean if the roots are complex?
- A: Complex roots often indicate that the model represented by the polynomial doesn't have a real-world interpretation within the context of the problem. However, they are still mathematically valid solutions.
-
Q: How accurate are numerical methods for finding roots?
- A: The accuracy of numerical methods depends on several factors, including the chosen method, the initial guess, and the number of iterations. Modern computational tools can achieve very high accuracy.
-
Q: Why is it important to understand cubic polynomials?
- A: Cubic polynomials are fundamental in modeling various real-world phenomena and solving numerous problems across different disciplines. Mastering the concepts surrounding them is essential for various scientific and engineering pursuits.
Conclusion: A Deeper Dive into Polynomial Analysis
Analyzing the cubic polynomial x³ + 4x² + 2x + 2 requires a multi-faceted approach. While finding exact solutions might involve complex formulas or iterative numerical methods, understanding its behavior and potential applications is equally crucial. This exploration highlights the importance of various algebraic techniques and underscores the power of numerical methods in solving problems where analytical solutions are elusive. Further exploration into numerical analysis and advanced algebraic techniques will enhance your ability to tackle more complex polynomials and their applications. The journey into understanding polynomial functions is a rich and rewarding one, opening doors to more advanced mathematical concepts and their real-world implications.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about X 3 4x 2 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.