X 4 Times X 2
disgrace
Sep 23, 2025 · 5 min read
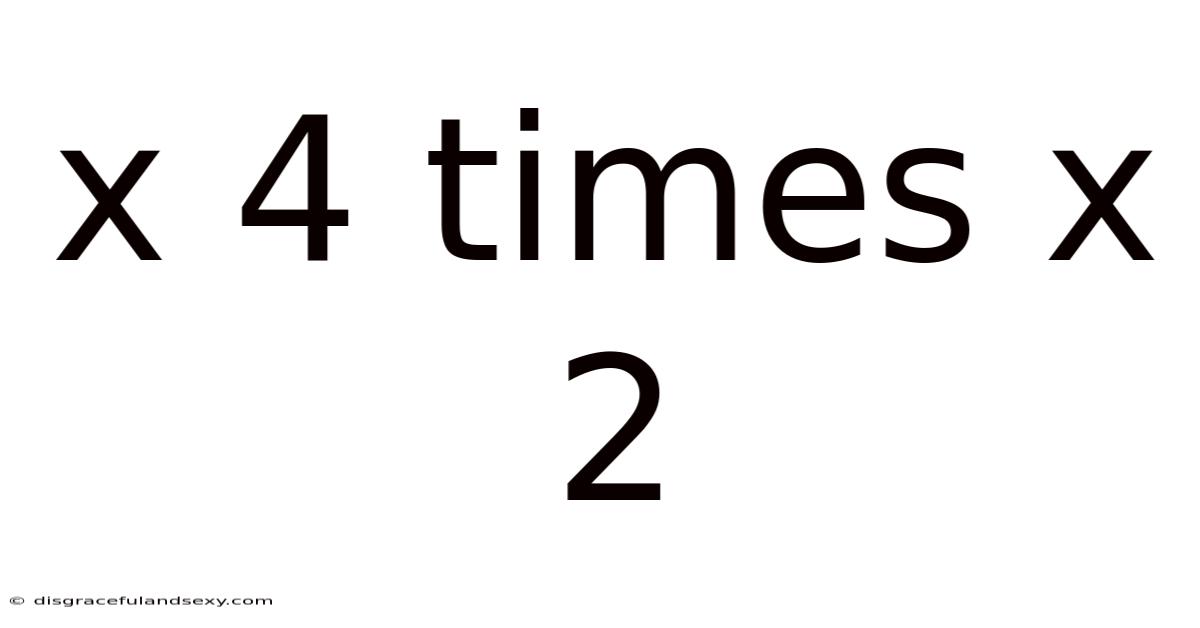
Table of Contents
Decoding the Mystery: x 4 Times x 2 – A Deep Dive into Repeated Multiplication
This article explores the mathematical concept represented by the expression "x 4 times x 2". We'll break down the meaning, delve into the different ways to approach this problem, explore its applications in various fields, and address common questions and misconceptions. This seemingly simple expression offers a gateway to understanding fundamental principles of algebra, exponents, and even the broader concept of repeated operations.
Understanding the Expression: x 4 Times x 2
At its core, the phrase "x 4 times x 2" describes a sequence of mathematical operations. It doesn't represent a single, concise calculation but rather a process. Let's dissect it:
-
"x 4 times": This signifies that a variable 'x' is being multiplied by itself four times. This can be written more compactly as x⁴ (x raised to the power of 4).
-
"x 2": This indicates a further multiplication of the result by 2.
Therefore, the full expression "x 4 times x 2" translates to: 2 * x⁴ or equivalently 2x⁴.
This seemingly straightforward translation opens the door to a wealth of possibilities and applications. We will now delve into different approaches to solving problems involving this type of expression.
Different Approaches and Solution Strategies
While the simplified expression 2x⁴ is clear, let's explore how we can arrive at this answer through different methods, particularly emphasizing clarity for those new to algebra.
1. The Step-by-Step Approach:
This approach is ideal for beginners. We perform the operations in the order implied:
- Multiply x four times: x * x * x * x = x⁴
- Multiply the result by 2: 2 * x⁴ = 2x⁴
This methodical approach highlights the order of operations and reinforces the fundamental concept of repeated multiplication.
2. The Exponent Approach:
This approach leverages the power of exponents. Recognizing that "x 4 times" is x⁴ immediately streamlines the process:
- Represent repeated multiplication with an exponent: x * x * x * x = x⁴
- Multiply by 2: 2 * x⁴ = 2x⁴
This method demonstrates efficiency and emphasizes the importance of understanding exponential notation.
3. The Distributive Property (though not directly applicable here):
While not directly applicable in this specific instance, understanding the distributive property is crucial for similar but more complex expressions. The distributive property states that a(b + c) = ab + ac. This becomes highly relevant when dealing with expressions such as 2(x⁴ + y²) where it allows us to distribute the 2 to both terms within the parenthesis.
Applications Across Diverse Fields
The seemingly simple expression 2x⁴ finds applications in various fields, often in more complex contexts:
1. Physics and Engineering:
-
Calculating Work Done: In physics, work is often expressed as force multiplied by distance. If the force applied varies with the square of a distance (x²), and this force is applied over a distance x², the total work done could be represented by an expression similar to 2x⁴, demonstrating the power of repeated multiplication in realistic scenarios.
-
Modeling Complex Systems: Engineers use such expressions as building blocks in creating mathematical models that describe complex dynamic systems. For example, in fluid dynamics or structural mechanics, polynomial expressions (expressions with exponents) are often encountered.
2. Computer Science:
-
Algorithmic Complexity: In analyzing the efficiency of algorithms, the time it takes to execute an algorithm often grows with the input size (n) raised to a power. Expressions like O(n⁴) (Big O notation), indicating that the runtime grows proportionally to n⁴, are common in algorithm analysis. The constant factor (2 in our case) may not always be critical, but the dominating term (n⁴) indicates the overall efficiency.
-
Data Structures and Memory Management: The memory space occupied by certain data structures might depend on the size of data raised to a power. Understanding such relationships is vital for efficient memory usage in programs.
3. Economics and Finance:
-
Compound Interest: The principle of compound interest, where interest earned is added to the principal, leading to exponential growth over time, is modeled using exponential functions. While not precisely 2x⁴, the underlying principle of repeated multiplication is similar.
-
Economic Modeling: Economic models often use polynomial functions, incorporating terms similar to our expression, to describe various relationships between economic variables such as production, consumption, and investment.
4. Mathematics Itself:
- Polynomial Equations: Our expression is a simple example of a polynomial, a mathematical expression involving variables raised to non-negative integer powers. Understanding simpler polynomials like 2x⁴ is foundational for tackling more advanced polynomial equations and their solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What if the expression was "x times x times x times x times 2"?
A1: This is equivalent to 2x⁴, the same result as "x 4 times x 2." The order of multiplication does not affect the final result because multiplication is commutative (the order of operands doesn't change the outcome).
Q2: How do I solve for x if 2x⁴ = 32?
A2: To solve for x, you would:
- Divide both sides by 2: x⁴ = 16
- Take the fourth root of both sides: x = ±2 (Both +2 and -2 raised to the power of 4 equal 16).
Q3: What happens if x is a negative number?
A3: If x is negative, x⁴ will be positive because an even number of negative factors results in a positive product. For example, if x = -2, then 2x⁴ = 2(-2)⁴ = 2(16) = 32.
Q4: Can this expression be simplified further?
A4: In its current form (2x⁴), the expression is already simplified. It's a monomial (a single term) with a coefficient of 2 and a variable raised to a power.
Conclusion: The Power of Repeated Multiplication
The seemingly simple expression "x 4 times x 2," which simplifies to 2x⁴, reveals much about the fundamental principles of mathematics, particularly the power of repeated multiplication. Understanding this expression, and how to manipulate it, opens doors to more advanced mathematical concepts and empowers us to solve problems across a wide range of disciplines. From the precise calculations needed in engineering to the abstract models in economics, the ability to handle repeated multiplication and exponential expressions is an invaluable skill. This exploration serves as a stepping stone towards deeper mathematical understanding and problem-solving prowess. The journey beyond this simple example leads to a richer appreciation of the elegance and power of mathematics in understanding and shaping our world.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about X 4 Times X 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.