Y 2x 2 4x 6
disgrace
Sep 13, 2025 · 7 min read
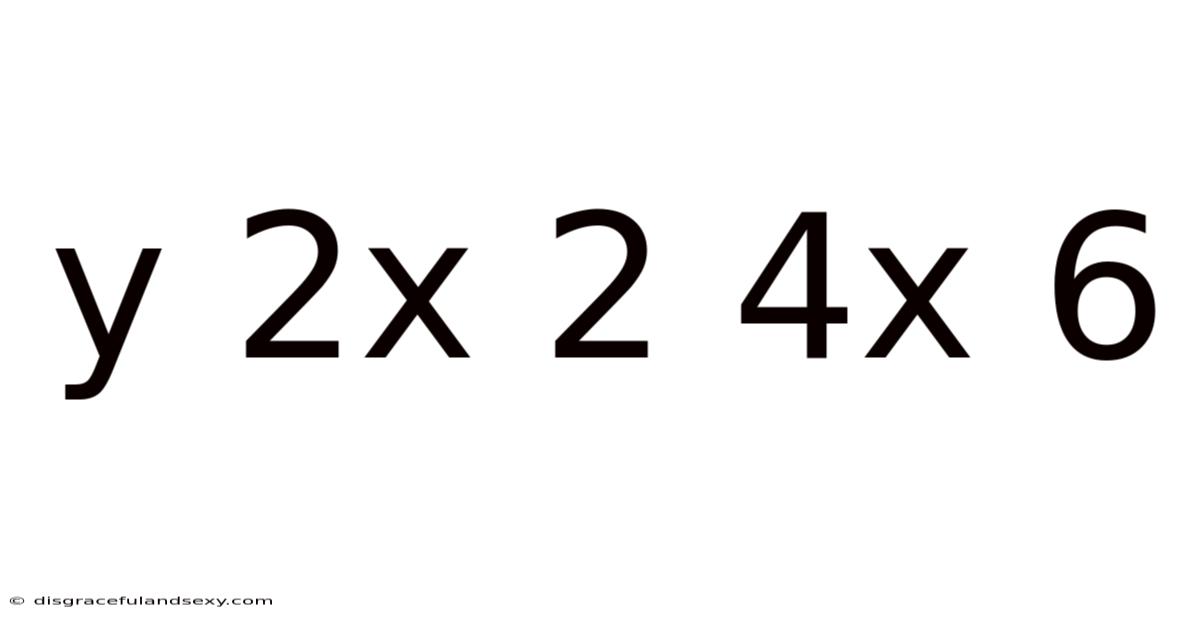
Table of Contents
Unveiling the Mystery: A Deep Dive into the Mathematical Expression "y = 2x² + 4x + 6"
This article explores the quadratic equation y = 2x² + 4x + 6, delving into its properties, graphical representation, and practical applications. Understanding this seemingly simple equation unlocks a gateway to comprehending more complex mathematical concepts. We will cover everything from basic algebraic manipulation to more advanced topics like finding the vertex, axis of symmetry, and interpreting the parabola's characteristics. Whether you're a high school student grappling with algebra or a curious individual wanting to refresh your mathematical knowledge, this comprehensive guide will equip you with the tools to master this fundamental concept.
Introduction: Understanding Quadratic Equations
A quadratic equation is a second-degree polynomial equation of the form ax² + bx + c = 0, where 'a', 'b', and 'c' are constants, and 'a' is not equal to zero. Our focus, y = 2x² + 4x + 6, is a quadratic function, which is a slight variation; instead of equaling zero, it's expressed in terms of 'y', representing the output or dependent variable. This allows us to visualize the equation as a curve on a graph, rather than just finding the roots (where the equation equals zero). Understanding quadratic functions is crucial in various fields, from physics (projectile motion) to economics (modeling cost and revenue).
Graphical Representation: The Parabola
The graph of a quadratic function is always a parabola, a U-shaped curve. The parabola's shape is determined by the coefficient of the x² term (in our case, 'a' = 2). Since 'a' is positive (2 > 0), our parabola opens upwards, meaning it has a minimum point (vertex). If 'a' were negative, the parabola would open downwards, having a maximum point.
Let's break down the key features of the parabola represented by y = 2x² + 4x + 6:
-
Vertex: The vertex is the lowest point (minimum) on the parabola. Finding the vertex is crucial for understanding the equation's behavior. The x-coordinate of the vertex can be found using the formula: x = -b / 2a. In our equation, a = 2 and b = 4, so x = -4 / (2 * 2) = -1. Substituting x = -1 back into the original equation gives us the y-coordinate: y = 2(-1)² + 4(-1) + 6 = 4. Therefore, the vertex is at the point (-1, 4).
-
Axis of Symmetry: The axis of symmetry is a vertical line that divides the parabola into two symmetrical halves. It passes through the vertex. The equation of the axis of symmetry is simply x = -1 (the x-coordinate of the vertex).
-
y-intercept: The y-intercept is the point where the parabola intersects the y-axis. This occurs when x = 0. Substituting x = 0 into the equation gives y = 6. So, the y-intercept is at the point (0, 6).
-
x-intercepts (Roots): The x-intercepts, also known as roots or zeros, are the points where the parabola intersects the x-axis (where y = 0). To find these, we set y = 0 and solve the quadratic equation 2x² + 4x + 6 = 0. We can simplify this equation by dividing by 2: x² + 2x + 3 = 0. This quadratic equation doesn't factor easily, so we'll use the quadratic formula: x = [-b ± √(b² - 4ac)] / 2a. In this case, a = 1, b = 2, and c = 3. The discriminant (b² - 4ac) is 2² - 4(1)(3) = -8, which is negative. A negative discriminant indicates that there are no real x-intercepts; the parabola does not cross the x-axis. The roots are complex numbers.
Step-by-Step Analysis and Calculations
Let's systematically analyze the equation y = 2x² + 4x + 6:
-
Identify 'a', 'b', and 'c': In our equation, a = 2, b = 4, and c = 6.
-
Determine the direction of the parabola: Since a > 0, the parabola opens upwards.
-
Calculate the x-coordinate of the vertex: x = -b / 2a = -4 / (2 * 2) = -1.
-
Calculate the y-coordinate of the vertex: Substitute x = -1 into the equation: y = 2(-1)² + 4(-1) + 6 = 4. The vertex is (-1, 4).
-
Find the axis of symmetry: The axis of symmetry is x = -1.
-
Find the y-intercept: Set x = 0: y = 2(0)² + 4(0) + 6 = 6. The y-intercept is (0, 6).
-
Find the x-intercepts (roots): Use the quadratic formula or other methods to solve 2x² + 4x + 6 = 0. As discussed earlier, this equation has no real roots.
Advanced Concepts and Applications
Beyond the basic analysis, let's explore some more advanced concepts related to our quadratic function:
-
Completing the Square: This technique allows us to rewrite the quadratic equation in vertex form, y = a(x - h)² + k, where (h, k) is the vertex. Completing the square for y = 2x² + 4x + 6 involves factoring out the 'a' coefficient from the x terms: y = 2(x² + 2x) + 6. Then, we take half of the coefficient of x (which is 1), square it (1² = 1), and add and subtract this value inside the parenthesis: y = 2(x² + 2x + 1 - 1) + 6. This allows us to create a perfect square trinomial: y = 2((x + 1)² - 1) + 6. Simplifying, we get the vertex form: y = 2(x + 1)² + 4. This clearly shows the vertex at (-1, 4).
-
Calculus Applications: The derivative of a quadratic function gives us the slope of the tangent line at any point on the parabola. The derivative of y = 2x² + 4x + 6 is dy/dx = 4x + 4. Setting this to zero allows us to find the x-coordinate of the vertex (where the slope is zero).
-
Real-World Applications: Quadratic equations are used extensively in various fields. For instance, in physics, the trajectory of a projectile can be modeled using a quadratic equation. In engineering, quadratic equations are used to design parabolic antennas and reflectors. In economics, quadratic functions can model cost functions, revenue functions, and profit maximization.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What does the 'a' value (2 in this case) represent in the quadratic equation?
A1: The 'a' value determines the parabola's vertical stretch or compression and its direction. A positive 'a' means the parabola opens upwards, while a negative 'a' means it opens downwards. A larger absolute value of 'a' indicates a narrower parabola, while a smaller absolute value indicates a wider parabola.
Q2: Why are there no real x-intercepts for this equation?
A2: The lack of real x-intercepts stems from the negative discriminant (b² - 4ac = -8) in the quadratic formula. A negative discriminant indicates that the solutions to the quadratic equation are complex numbers (involving the imaginary unit 'i'). Geometrically, this means the parabola doesn't intersect the x-axis.
Q3: How can I find the range of the quadratic function?
A3: Since the parabola opens upwards and has a vertex at (-1, 4), the range is all y-values greater than or equal to 4. We can write this as: y ≥ 4.
Q4: Can this equation be used to model real-world scenarios?
A4: Yes, this equation, or similar quadratic equations, can model various phenomena, including projectile motion, the area of a rectangular region subject to constraints, or even simple economic models. The specific values of 'a', 'b', and 'c' would need to be adjusted to match the specific context.
Conclusion: Mastering Quadratic Functions
The seemingly simple equation y = 2x² + 4x + 6 provides a rich foundation for understanding quadratic functions. Through careful analysis of its properties – vertex, axis of symmetry, intercepts, and parabola shape – we can gain valuable insights into its behavior and applications. The techniques discussed, such as completing the square and using the quadratic formula, are essential tools for working with quadratic equations. Understanding these concepts opens doors to more advanced mathematical and scientific fields, enabling you to solve complex problems and model real-world phenomena. This exploration serves not only as a deep dive into this particular equation but also as a stepping stone to mastering the broader field of quadratic functions and their diverse applications. Remember that persistent practice and a curious mind are key to unlocking the full potential of mathematics.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Y 2x 2 4x 6 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.