Y 2x 2 8x 5
disgrace
Sep 13, 2025 · 6 min read
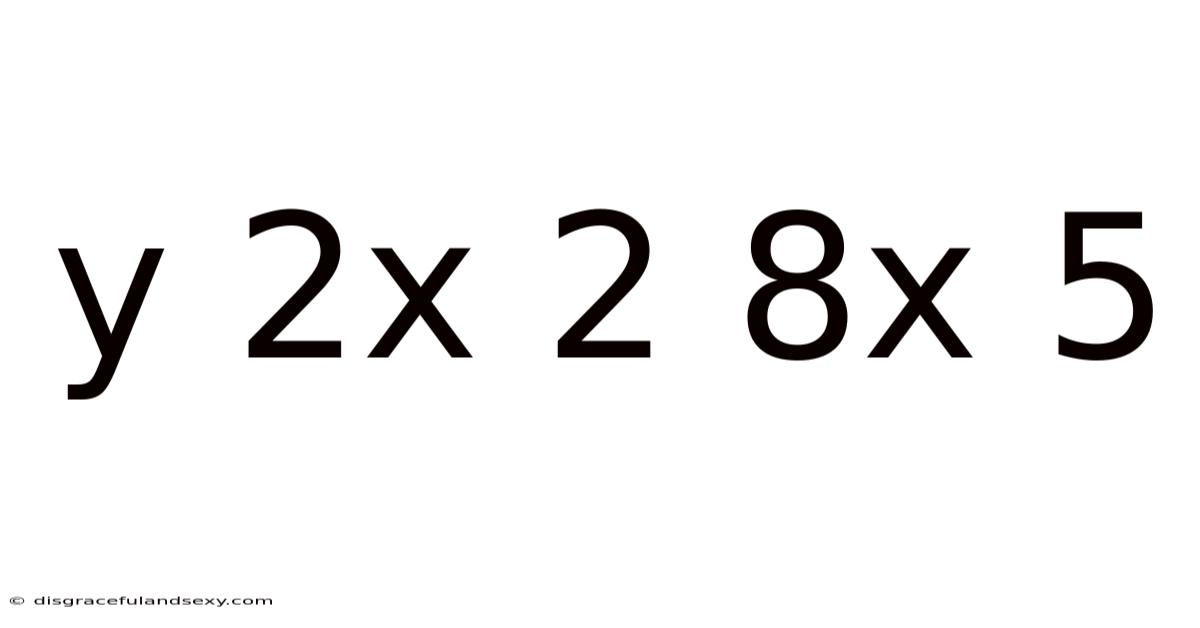
Table of Contents
Decoding the Mathematical Expression: y = 2x² + 8x + 5
This article delves into the mathematical expression y = 2x² + 8x + 5, exploring its various facets, from basic understanding to advanced applications. We'll cover identifying the type of function, finding its vertex, determining its intercepts, and sketching its graph. We will also explore the broader context of quadratic equations and their significance in mathematics and various real-world applications. Understanding this seemingly simple equation unlocks a deeper understanding of quadratic functions and their power in modeling various phenomena.
Introduction: Understanding Quadratic Functions
The equation y = 2x² + 8x + 5 represents a quadratic function. A quadratic function is a polynomial function of degree two, meaning the highest power of the variable (x in this case) is 2. These functions are characterized by their parabolic graphs, exhibiting a distinctive U-shape (opening upwards if the coefficient of x² is positive, and downwards if negative). The general form of a quadratic function is:
y = ax² + bx + c
Where 'a', 'b', and 'c' are constants, and 'a' is not equal to zero (otherwise, it wouldn't be a quadratic function). In our specific equation, a = 2, b = 8, and c = 5.
Identifying Key Features of the Quadratic Function y = 2x² + 8x + 5
Understanding the key features of a quadratic function allows us to accurately represent it graphically and analytically. These key features include:
-
Vertex: The vertex is the lowest (or highest, depending on the parabola's orientation) point on the parabola. It represents the minimum or maximum value of the function. The x-coordinate of the vertex can be found using the formula: x = -b / 2a. In our equation, this gives us x = -8 / (2 * 2) = -2. Substituting x = -2 back into the original equation gives us the y-coordinate: y = 2(-2)² + 8(-2) + 5 = -3. Therefore, the vertex is (-2, -3).
-
Axis of Symmetry: The axis of symmetry is a vertical line that passes through the vertex, dividing the parabola into two symmetrical halves. Its equation is simply x = -b / 2a, which is the same as the x-coordinate of the vertex. In our case, the axis of symmetry is x = -2.
-
x-intercepts (Roots or Zeros): The x-intercepts are the points where the parabola intersects the x-axis (where y = 0). To find these, we set y = 0 and solve the quadratic equation:
2x² + 8x + 5 = 0
This quadratic equation can be solved using the quadratic formula:
x = [-b ± √(b² - 4ac)] / 2a
Substituting our values (a = 2, b = 8, c = 5), we get:
x = [-8 ± √(8² - 4 * 2 * 5)] / (2 * 2) = [-8 ± √(24)] / 4 = [-8 ± 2√6] / 4 = -2 ± √6/2
Therefore, the x-intercepts are approximately x ≈ -0.775 and x ≈ -3.225.
-
y-intercept: The y-intercept is the point where the parabola intersects the y-axis (where x = 0). To find this, we simply substitute x = 0 into the equation:
y = 2(0)² + 8(0) + 5 = 5
Therefore, the y-intercept is (0, 5).
Graphing the Quadratic Function
With the key features identified, we can now accurately sketch the graph of y = 2x² + 8x + 5. The parabola opens upwards (since a = 2 > 0), has a vertex at (-2, -3), an axis of symmetry at x = -2, x-intercepts at approximately -0.775 and -3.225, and a y-intercept at (0, 5). Plotting these points and sketching a smooth U-shaped curve through them will give you the graph of the quadratic function.
Solving Quadratic Equations: Different Approaches
Solving quadratic equations, like the one we encountered when finding the x-intercepts, is a fundamental skill in algebra. Besides the quadratic formula, other methods exist:
-
Factoring: This method involves expressing the quadratic expression as a product of two linear expressions. Not all quadratic equations can be factored easily, however. For example, 2x² + 8x + 5 cannot be easily factored using integers.
-
Completing the Square: This technique involves manipulating the quadratic expression to create a perfect square trinomial, making it easier to solve. While applicable to our equation, it’s often less straightforward than the quadratic formula for complex equations.
-
Graphing: The x-intercepts of the graph directly represent the solutions to the quadratic equation. This method is particularly useful for visualizing the solutions.
Real-World Applications of Quadratic Functions
Quadratic functions are not just abstract mathematical concepts; they have numerous real-world applications across various fields:
-
Physics: Projectile motion (e.g., the trajectory of a ball thrown in the air) is often modeled using quadratic equations. The height of the projectile at any given time can be described by a quadratic function.
-
Engineering: Architects and engineers use quadratic functions to design parabolic arches and structures, taking advantage of the parabola's strength and stability.
-
Economics: Quadratic functions can be used to model cost functions, revenue functions, and profit functions in business and economics. Finding the vertex of these functions can help determine the optimal production level for maximum profit.
-
Computer Graphics: Parabolic curves are used in computer graphics to create smooth, realistic curves in images and animations.
-
Data Analysis: Quadratic regression analysis can be used to fit a quadratic model to a set of data points, allowing for predictions and analysis of trends.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What does the coefficient 'a' in a quadratic function represent?
A: The coefficient 'a' determines the parabola's orientation (upwards if a > 0, downwards if a < 0) and its vertical stretch or compression. A larger absolute value of 'a' indicates a narrower parabola, while a smaller absolute value indicates a wider parabola.
Q: Can a quadratic function have only one x-intercept?
A: Yes, if the discriminant (b² - 4ac) in the quadratic formula is equal to zero, the parabola will touch the x-axis at only one point, meaning the quadratic equation has one repeated root.
Q: What is the relationship between the vertex and the axis of symmetry?
A: The axis of symmetry always passes through the vertex of the parabola. The x-coordinate of the vertex is the same as the equation of the axis of symmetry.
Q: How can I find the maximum or minimum value of a quadratic function?
A: The y-coordinate of the vertex represents the maximum or minimum value of the function. If the parabola opens upwards (a > 0), the vertex represents the minimum value; if it opens downwards (a < 0), the vertex represents the maximum value.
Q: Are there any limitations to using quadratic functions for modeling real-world phenomena?
A: While quadratic functions are powerful tools, they may not always accurately represent complex real-world scenarios. More complex functions might be needed to capture nuances and non-linear relationships.
Conclusion: The Significance of Understanding Quadratic Functions
The equation y = 2x² + 8x + 5, while seemingly simple, provides a gateway to understanding the broader world of quadratic functions. By learning to identify key features, solve quadratic equations, and appreciate their real-world applications, we can unlock a deeper understanding of mathematical modeling and its impact across various disciplines. The ability to analyze and interpret quadratic functions is a valuable skill that transcends the boundaries of mathematics, extending into fields like science, engineering, economics, and beyond. The thorough exploration of this single equation underscores the significance of mastering fundamental mathematical concepts and their practical relevance. The journey of understanding this specific equation is a microcosm of the power of mathematics to illuminate and explain the world around us.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Y 2x 2 8x 5 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.